The IMPACT Study: Impact of Time to Receipt of Prosthesis on Total Healthcare Costs 12 Months Post-amputation

Journal
American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Read Online
Authors
Taavy A Miller, MSPO1,2, Rajib Paul1, PhD, Melinda Forthofer, PhD1, Shane R. Wurdeman, PhD2,3
- Department of Public Health, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC, USA
- Department of Clinical and Scientific Affairs, Hanger Clinic, Austin, TX, USA
- Department of Biomechanics, University of Nebraska at Omaha, Omaha, NE, USA
Objective
Assess the impact of a prosthesis and the timing of prosthesis receipt on total direct health care costs in the 12 months post-amputation period
Design
Data on patients with lower limb amputation (n=510) were obtained from a national commercial adjudicated claims (Watson) database for retrospective cohort analysis which includes all inpatient and outpatient claims.
Patient Inclusion Criteria:
- Lower limb amputation
- Continually insured
Patient Demographics:
- Between ages of 18 – 64
- 75% had a Transtibial amputation (p<0.0001)
- 70% were male (p=0.06)
- 64% were diabetic or had vascular disease (p=0.11)
Results
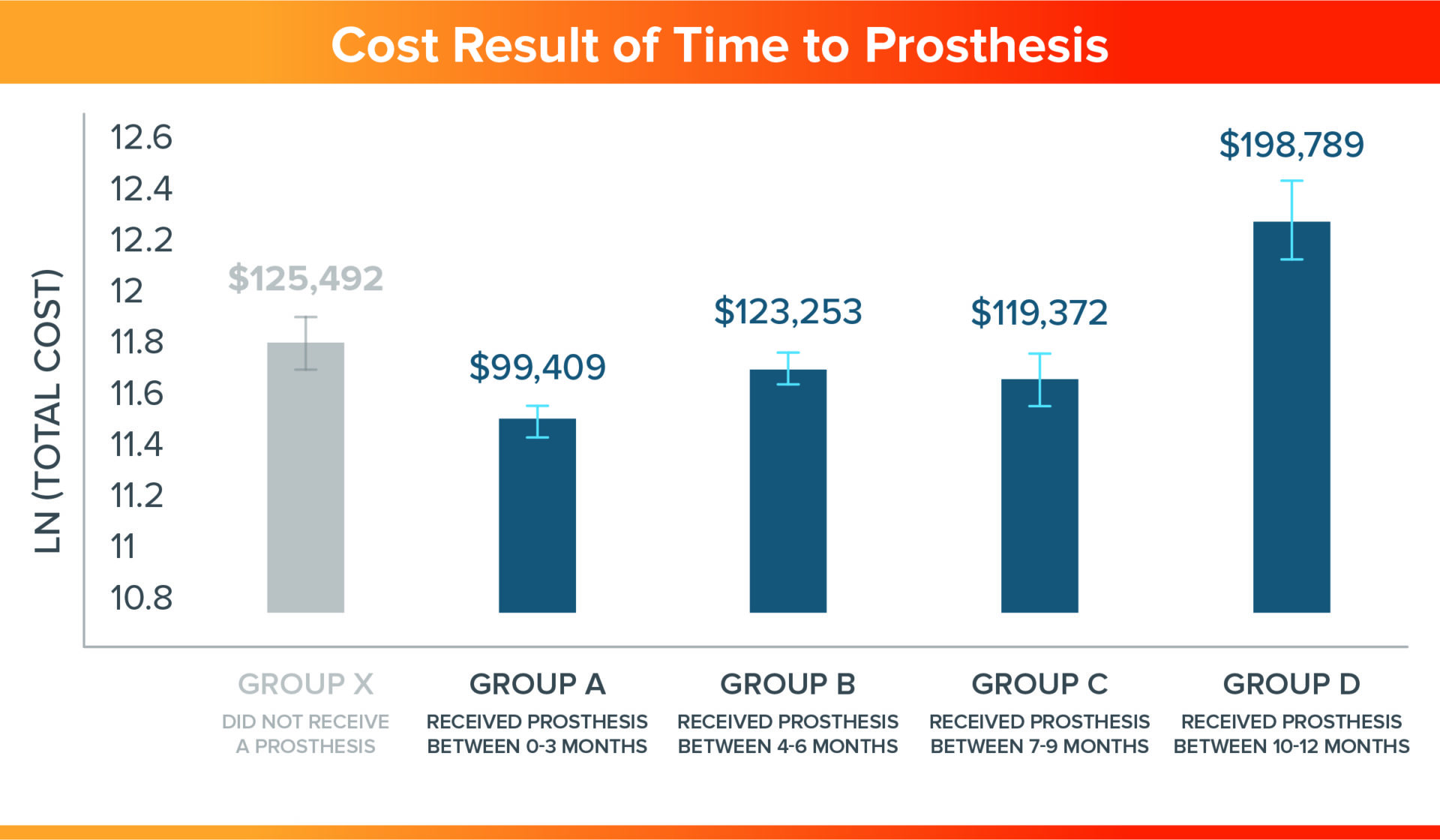
- Patients who received a prosthesis between 0-3 months (Group A) post amputation saved 25% in healthcare costs as compared to those who did not receive a prosthesis (Group X) (p=0.044)
- Average total healthcare costs were similar for individuals receiving their prosthesis between 4-6 months (Group B) and 7-9 months (Group C), including the cost of a prosthesis and those who did not receive a prosthesis (Group X).
- There is considerable economic value in providing a prosthesis prior to 10 months post-amputation, resulting from prosthetic mobility and quality of life.
Conclusion
- Economic burdens associated with healthcare for those with chronic health conditions and aging population remains high.
- The clinical benefits of prosthetic rehabilitation can actually serve to potentially reduce other non-prosthetic costs.
- Age, Sex and Diabetes/Vascular status alone are not drivers of total healthcare costs in the 12 months following amputation.
- Early delivery of a prosthesis, post amputation, is associated with reduced overall direct healthcare costs in addition to the physical, social and mental benefits of receiving a prosthesis.
About Watson: The Watson database is a large US private sector health claims database containing de-identified records representing approximately 25% of all commercial claims aggregated into one database with patient-level enrollment history, medical, and pharmacy commercials claims nationwide.
Authors from Hanger Clinic

Shane Wurdeman, PhD, CP, FAAOP (D)
Director, Clinical Research, Hanger Clinic
Dr. Wurdeman has published numerous studies in peer-reviewed journals. In addition to his research work, he continues to manage a patient case load with Hanger Clinic.

Taavy A. Miller, MSPO, CPO
After earning her MSPO and working as a CPO, Taavy transitioned into teaching O&P and then returned full time to earn her PhD in health services research. She has published several studies in peer-reviewed journals, presented abstracts at various conferences, and currently works as a research scientist conducting and leading research projects with a focus on patient outcomes.
Latest Updates
Subscribe to stay up-to-date on our latest posts.


